Question Type 1
When Three/Four positions of a single dice are given and we are supposed to find out opposite face(s)
Step 1: Select two positions of the same dice.
Step 2: Now solve by applying the rules that we learnt to find out opposite faces when two positions of the dice are given.
The key is to select the two relevant positions of the dice.
Three positions given
Q. In the following question, three positions of the same dice are given. What will be the digit on the opposite to the face having digit 5?
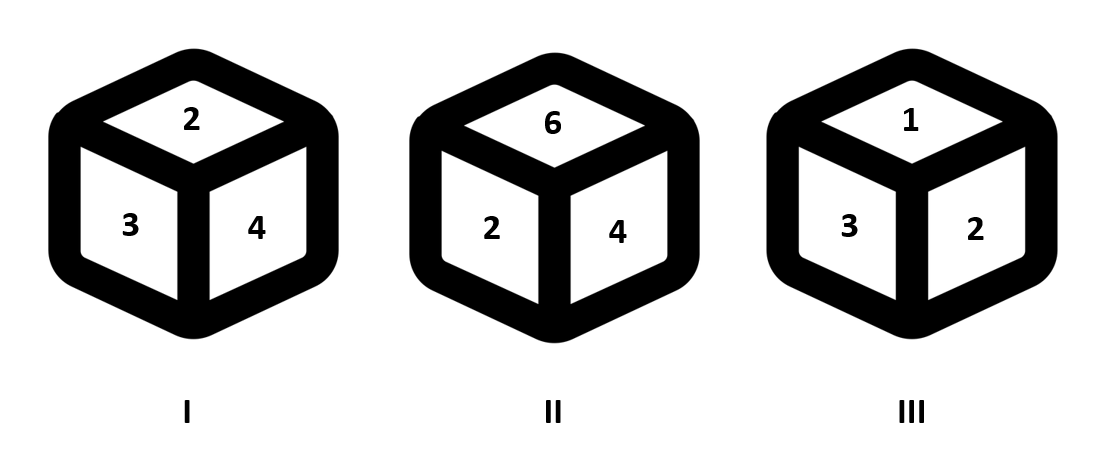
(a) 6 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 2Explanations :
Explanation 1: Choosing dices having 2 common faces
Taking dices I and III, 2 and 3 are common. So, 4 will be opposite to 1.
Taking dices I and II, 2 and 4 are common. So, 6 will be opposite to 3.
Hence, 5 must be opposite to 2.
Note: As you can see, one drawback of this method is that we sometimes have to apply it twice.
Taking dices I and III, 2 and 3 are common. So, 4 will be opposite to 1.
Taking dices I and II, 2 and 4 are common. So, 6 will be opposite to 3.
Hence, 5 must be opposite to 2.
Note: As you can see, one drawback of this method is that we sometimes have to apply it twice.
Four positions given
Q. Four positions of a dice are given below. Identify the number at the bottom when the number at the top is 1.
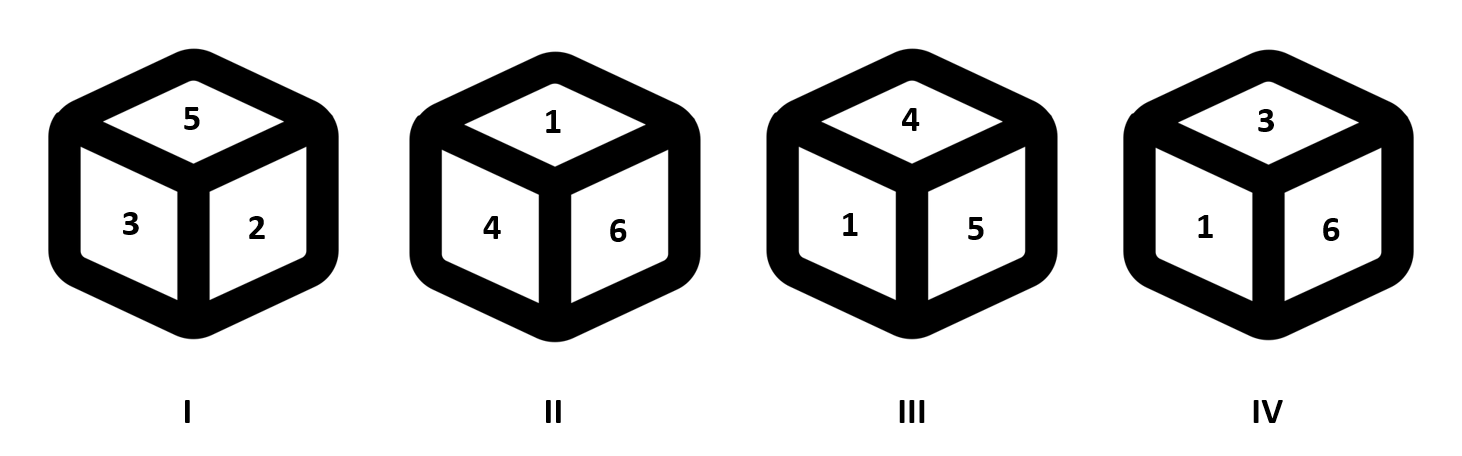
(a) 6 (b) 3 (c) 2 (d) 5Explanations :
Explanation 1: Choosing dices having 2 common faces
Taking dices II and III, 1 and 4 are common. So, 5 will be opposite to 6.
Taking dices II and IV, 1 and 6 are common. So, 3 will be opposite to 4.
Hence, 1 must be opposite to 2. If 1 is at the top, then obviously 2 will be at the bottom.
Note: As you can see, one drawback of this method is that we sometimes have to apply it twice.
Taking dices II and III, 1 and 4 are common. So, 5 will be opposite to 6.
Taking dices II and IV, 1 and 6 are common. So, 3 will be opposite to 4.
Hence, 1 must be opposite to 2. If 1 is at the top, then obviously 2 will be at the bottom.
Note: As you can see, one drawback of this method is that we sometimes have to apply it twice.