Direction and Distance
Direction
Direction - measurement of position of one thing with respect to a reference point.
Directions can be of two types:
- Relative direction - position of one thing with respect to some other thing or point.
- Absolute direction - position of one thing with respect to the orientation of the Earth, i.e. geographical North, South, East and West (here the reference point is the Sun).
For example:
A couple is sitting by a lake watching the sunset.
 The direction they are facing is West (Sun sets in the West). So, their absolute direction is West.
The direction they are facing is West (Sun sets in the West). So, their absolute direction is West.
But their relative directions with respect to each other will be different. The male is to the North of the female and the female is to the South of the male.
Distance
Distance - the length of the space between two points.
Distances can be of two types too:
- Total distance travelled from point A to Point B.
- Shortest distance between point A to Point B. This will generally be a straight line joining the two points.
For example:
Consider a person has to travel from Mumbai to Delhi, via Bhopal.
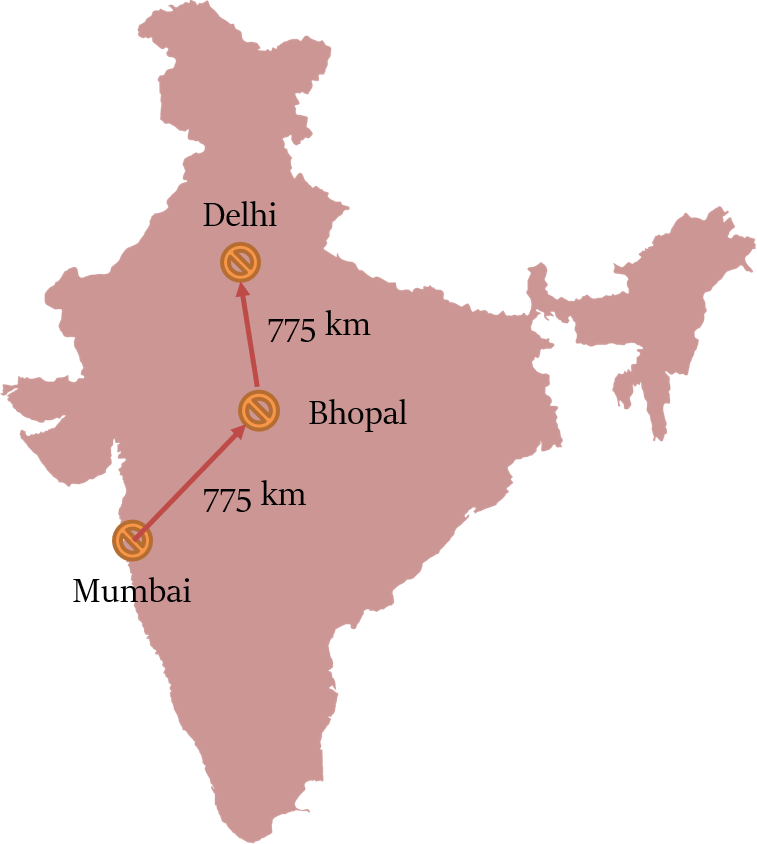 Then, total distance travelled by the person = Distance between Mumbai & Bhopal + Distance between Bhopal & Delhi = 775 + 775 = 1550 km
Then, total distance travelled by the person = Distance between Mumbai & Bhopal + Distance between Bhopal & Delhi = 775 + 775 = 1550 km
But the shortest distance between Mumbai & Delhi will be the length of the straight line joining the two cities.
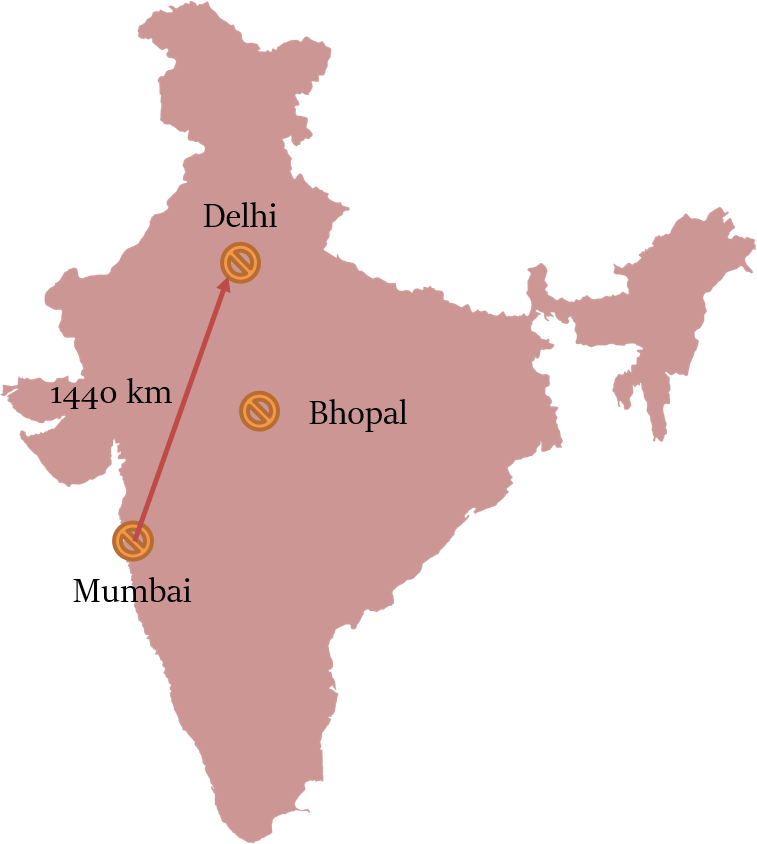 If a person travels via a direct flight from Mumbai to Delhi, then he will have to travel only 1400 km.
If a person travels via a direct flight from Mumbai to Delhi, then he will have to travel only 1400 km.
So, in this chapter your sense of direction and distance travelled will be put under scrutiny.
Types of questions in this chapter:
- Finding only the direction
- Finding only the distance
- Finding both the distance and direction