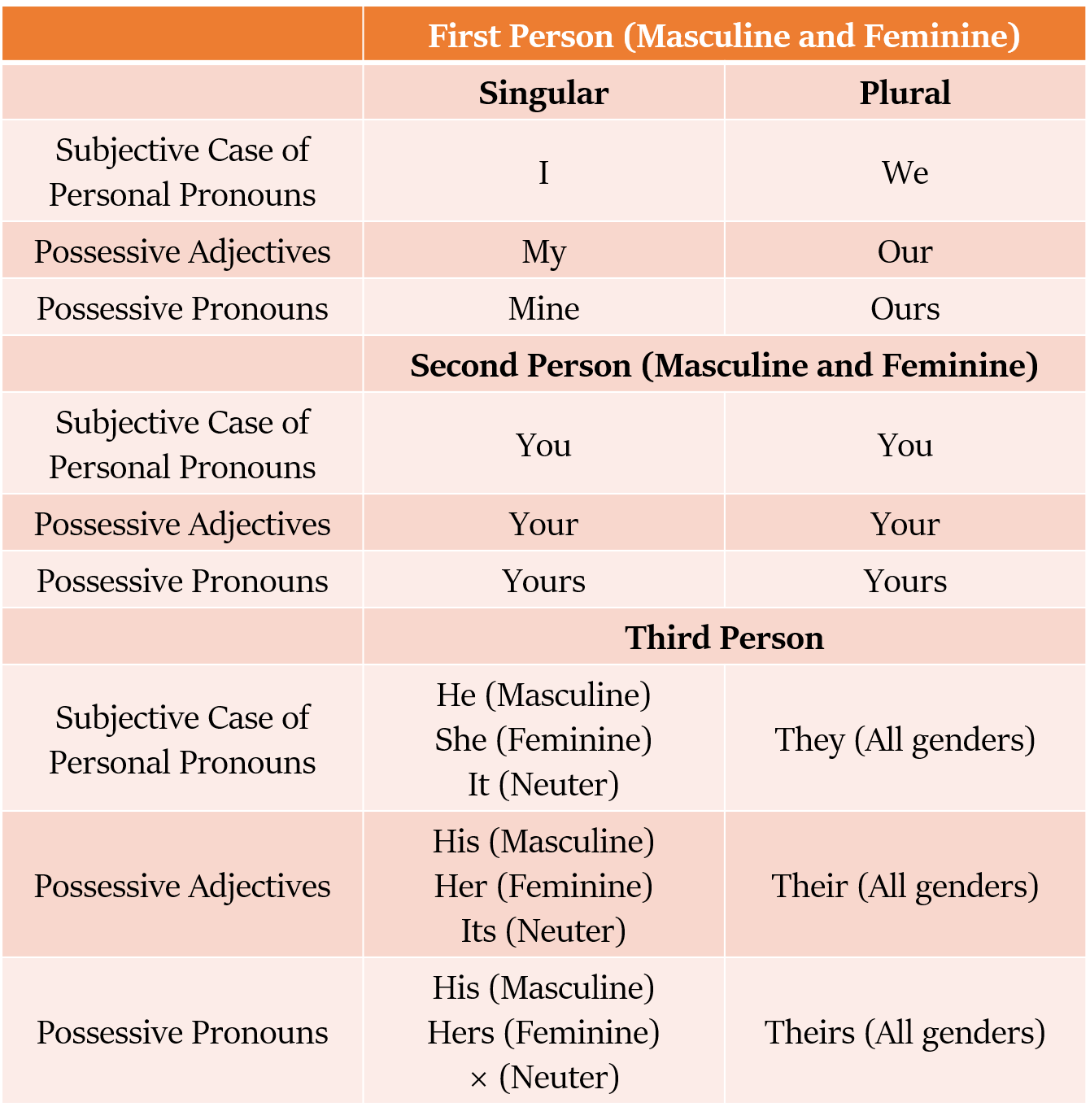
Possessive case of Personal pronouns
Possessive Cases of most of the Personal Pronouns have two forms:
Possessive Adjectives
Possessive Pronouns
‘His’ is used as both Possessive Adjective and Possessive Pronoun.
This is his bike. (Possessive Adjective)
This bike is his. (Possessive Pronoun)
‘Her’ is used as both Objective case and Possessive Adjective.
I gave my bike to her. (Objective case)
This is her bike. (Possessive Adjective)
‘Its’ is used as Possessive Adjective but not as Possessive Pronoun.
Possessive Adjectives
Possessive adjectives are used to show possession/relation.
my, our, your, his, her, its, their – they are Possessive adjectives because they come with a noun and modify them.
This is my bike.
Those are your bikes.
That is her bike.
Possessive Pronouns
Just like Possessive adjectives, Possessive pronouns also show possession.
E.g. mine, ours, yours, his, hers, theirs
This bag is mine.
Those balls are yours.
Possessive Adjectives Vs. Possessive Pronouns
You will notice that Possessive pronoun is nothing but : Possessive Adjective + Noun
E.g. my + noun → mine ; our + noun → ours
your + noun → yours
his + noun → his ; her + noun → hers
their + noun → theirs
Possessive adjective is always followed by noun or noun equivalent. It is never used without a noun.
On the other hand, Possessive pronoun can never qualify a noun (as possessive pronoun is already used in place of a noun). We will use possessive pronoun in a sentence if the noun has already been discussed in the sentence (to avoid repetition).
Examples:
This book is my. (incorrect; my – possessive adjective, but not followed by a noun)
This is my book. (correct; my – possessive adjective, followed by a noun ‘book’)
This book is mine. (correct; mine – possessive pronoun)
Your brother is an inspector but mine brother is a minister. (incorrect; mine – possessive pronoun, cannot qualify a noun)
Your brother is an inspector but mine is a minister. (correct)
Your brother is an inspector but my brother is a minister. (correct)
Some books refer both Possessive Adjectives and Possessive Pronouns as Possessive Pronouns only. As per them, there are two types of Possessive Pronouns:
- Dependent form of Possessive Pronouns, i.e. those Possessive pronouns that need a noun.
- Independent form of Possessive Pronouns, i.e. those Possessive pronouns that do not need a noun.
More concepts related to Possessive Adjectives & Possessive Pronouns
Concept 1: Apostrophe
In Possessive Pronouns and Possessive Adjectives, apostrophe is not used before ‘s’.
It is incorrect to use - your’s, her’s, etc.
For example:
The leopard had a thorn in it’s foot. (incorrect; it’s is equivalent to ‘it is’)
The leopard had a thorn in its foot. (correct)
Concept 2: Use with to-infinitive
We can use either ‘
He forced me to leave.
They requested her to sing. (here, ‘her’ is in objective case, and not a possessive adjective.)
They wanted to hear him singing.
But we do not use ‘to +
Concept 3
We do not use possessive pronouns or possessive adjectives with separation, leave, excuse, mention, report, pardon, sight, favour.
His separation is very painful to me. (incorrect)
Separation from him is very painful to me. (correct)
We need your favour. (incorrect)
We need a favour from you. (correct)
Possessive pronouns as various parts of a sentence
Possessive pronoun can work as:
a subject:
Your life is good but hers is better.
My bike is a Harley, but his is a Triumph.an object:
She broke my heart so I broke hers.a subjective complement:
This country is mine.

Extra Books and Tools
If you prefer to learn via books, or want some good English Grammar books for reference purposes, you may read this article which enlists some of the books recommended by us.