Division and Distribution - Part II
In this article we will learn how to distribute items in groups of unknown sizes.
Unknown size groups mean that each group can have any number of items.
Distribution of distinct items
Number of ways to distribute n distinct items into r different groups = $r^n$
(we will count the number of ways n distinct items can be distributed, i.e. focus is on the number of options each of these n distinct items have. Each one of them have r options to get distributed; so r × r × r …. n times)
Note: If you remember, we covered it in the permutation article, wherein we saw the number of ways in which n distinct items can be distributed when repetition is allowed.
Distribution of identical items
If the items are identical then division and distribution is the same thing. We can only divide identical items. They can be arranged in only 1 way. No matter how you arrange identical items (after you already have divided them), the arrangement will look the same.
Number of ways to distribute n identical items into r different groups = $C^{n + r - 1}_{r - 1}$
(such that each group receives 0, 1, 2…. or n items, i.e. a group may or may not be left empty)
Number of ways to distribute n identical items into r different groups = $C^{n - 1}_{r - 1}$
(such that each group receives atleast one item, i.e. no group is left empty)
Memorizing the formulae is fine. But we would do ourselves a favour if we also try to understand the underlying concept.
We can understand this concept through various methods:
a. Linear Equation
b. Through visualization
Understanding in terms of Linear Equation
If we are given the following equation:
$x_1$ + $x_2$ + $x_3$ + ….. + $x_r$ = n (where n ≥ r), then
Number of positive integral solutions = $C^{n - 1}_{r - 1}$
To get non-negative integral solutions, we can write the above equation as:
(x1 + 1) + (x2 + 1) + (x3 + 1) + ….. + (xr + 1) = n + r
(We just added 1 to each of xi and added r on the right hand side to balance out the addition of r 1’s to the left hand side. We did so to ensure that even if xi is 0, xi + 1 will still be positive.)
Number of non-negative integral solutions = $C^{n + r - 1}_{r - 1}$
Note: If you look at this equation: $x_1$ + $x_2$ + $x_3$ + ….. + $x_r$ = n, you can see that even here we are distributing n identical items into r different groups (size of groups is not known). It’s just an algebraic way of representing the same real life scenario.
Note: There are infinite integral solutions of the above equation. But the number of positive (and non-negative) integral solutions is finite.
Understanding via Visualization
Let’s consider this equation: $x_1$ + $x_2$ + $x_3$ = 7
We have 7 identical items that need to be distributed among 3 different groups (size of groups is not known).
We can place these 7 identical items in a straight line. There are 6 inner gaps between these 7 items.
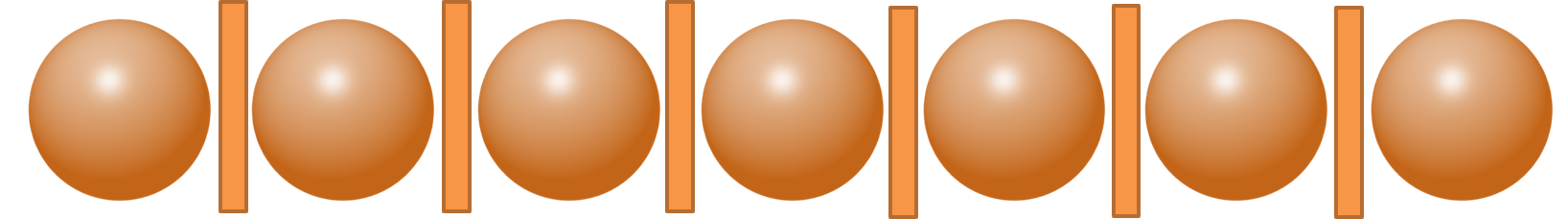
Now, let us try to find the positive and non-negative integral solutions.
Positive integral solutions
Let us find out the number of positive integral solutions.
Our equation is: $x_1$ + $x_2$ + $x_3$ = 7 (positive integral solutions means that $x_1$ or $x_2$ or $x_3$ cannot be zero)
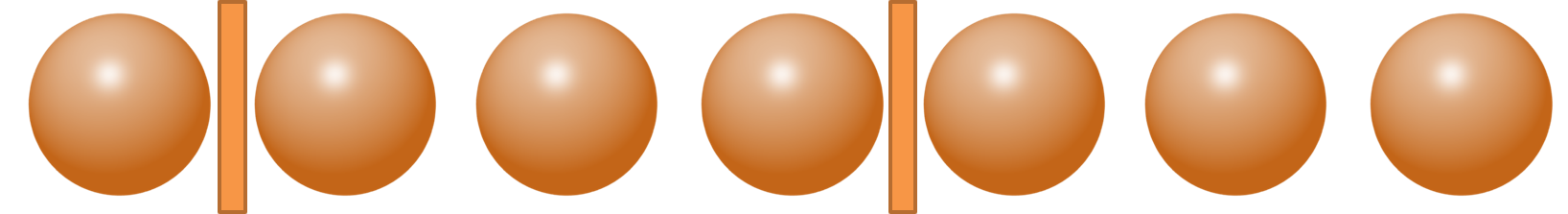
If we choose any two gaps, we are effectively dividing the 7 items into 3 groups.
So, we need to choose 2 gaps out of 6 inner gaps, which can be done in $C^6_2$ = 15 ways (Note: This is the same as applying the formula: $C^{n-1}_ {r-1}$ = $C^{7 - 1}_{3 - 1}$ = $C^6_2$ = 15 ways)
One such scenario has been represented in the figure below:
Non-negative integral solutions
Let us find out the number of non-negative integral solutions.
Our equation was: $x_1$ + $x_2$ + $x_3$ = 7 (non-negative integral solutions means that $x_1$ or $x_2$ or $x_3$ can be zero or more)
So, let us change our equation such that we get positive integral solutions. To do so, we need to eliminate the possibility of $x_1$ or $x_2$ or $x_3$ being zero. To do so, we will just add 1 to each one of them and balance the right hand side of the equation too.
So, ($x_1$ + 1) + ($x_2$ + 1) + ($x_3$ + 1) = 7 + 3 = 10
So, we just need to find the positive integral solutions of the above equation, just as we did before. There are 10 items now, so number of gaps will be 9.
So, we need to choose 2 gaps out of 9 total gaps, which can be done in $C^9_2$ = 36 ways
(Note: This is the same as applying the formula: $C^{n + r - 1}_ {r - 1}$ = $C^{7 + 3 - 1}_{3 - 1}$ = $C^9_2$ = 36 ways
There is one other way to visualize it.
Our equation is: $x_1$ + $x_2$ + $x_3$ = 7
If we choose any two gaps, we are effectively dividing the 7 items into 3 groups.
 But as we need to find non-negative integral solutions, some of the groups may have zero items too. So, we basically need to know the number of ways in which we can arrange these 9 things (7 identical items and 2 alike gaps).
But as we need to find non-negative integral solutions, some of the groups may have zero items too. So, we basically need to know the number of ways in which we can arrange these 9 things (7 identical items and 2 alike gaps).
It can be done in $C^9_2$ = 36 ways
Q. In how many ways can:
A. 5 different balls be distributed to 3 different boxes, when each box can contain any number of balls?
B. 5 identical balls be distributed to 3 different boxes, when each box can contain any number of balls?
Explanation:
B. Number of ways to distribute n identical items into r different groups = $C^{n + r - 1}_ {r - 1}$
(such that each group receives 0, 1, 2…. or n items, i.e. a group may or may not be left empty)
= $C^{5 + 3 - 1}_{3 - 1}$ = $C^7_2$ = 21