Mensuration - Prism
What is a Prism?
A Prism is a three dimensional polyhedron, such that:
- its two bases are similar, equal, and parallel polygons (of any number of sides), and
- the other faces are parallelograms, joining corresponding sides of the two bases.
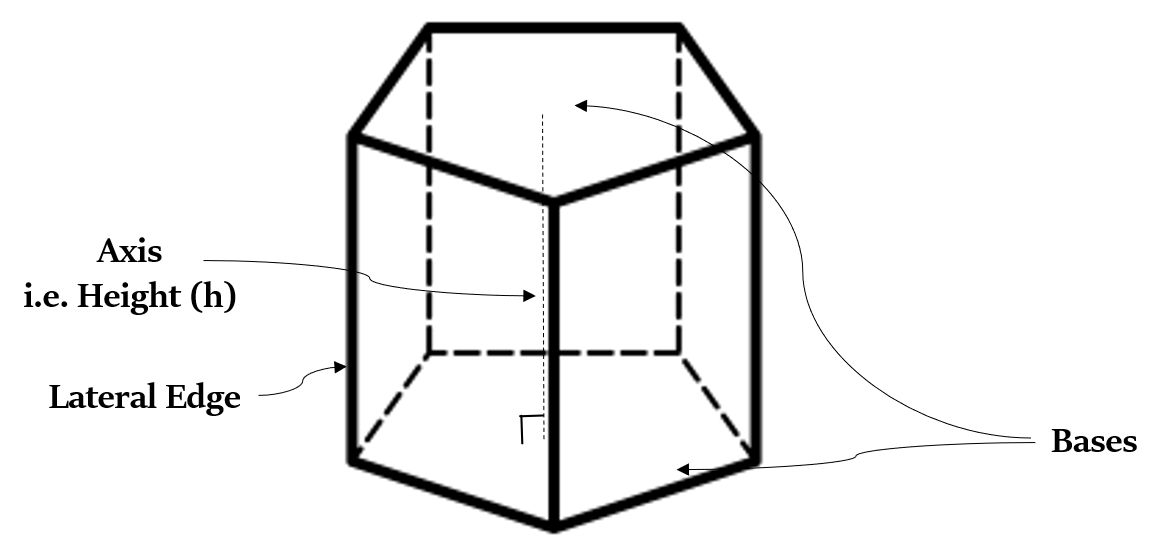
Lateral Faces - These are the faces other than the bases of a prism.
Lateral Edges - These are the lines of intersection of the lateral faces of a prism.
Axis of a Prism - It is the straight line joining the centres of the two bases of a prism. As the two bases are exactly similar and parallel to each other, the axis will be perpendicular to the two bases. The length of axis is called the height of the prism.
A prism with n-sided bases has 2n vertices, n + 2 faces, and 3n edges.
For example, in the above figure the bases have 5 sides, and so the prism has 10 vertices, 7 faces, and 15 edges.
Right Prism: It is a prism whose lateral edges are perpendicular to its bases.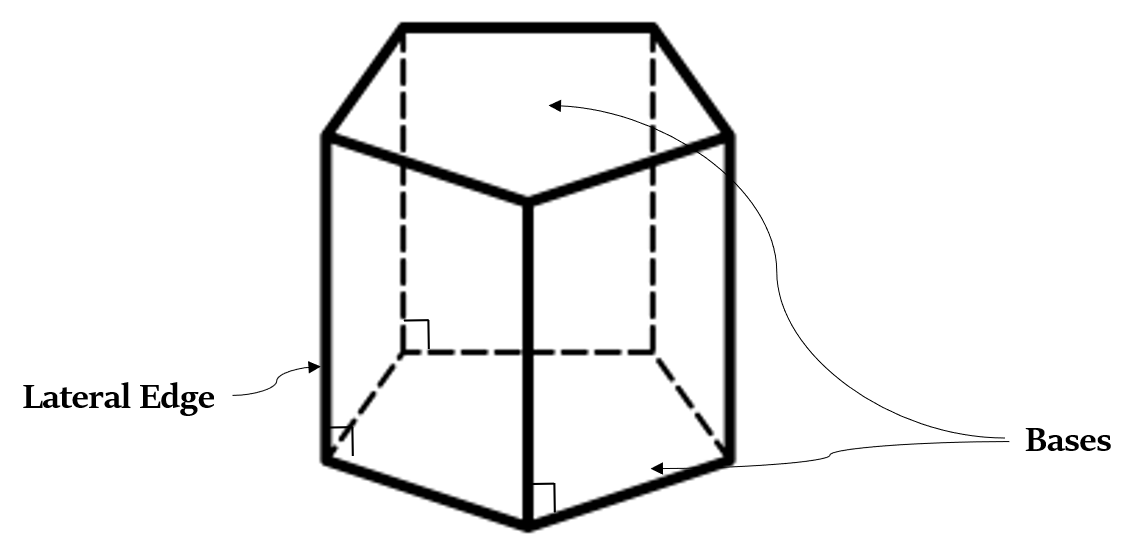
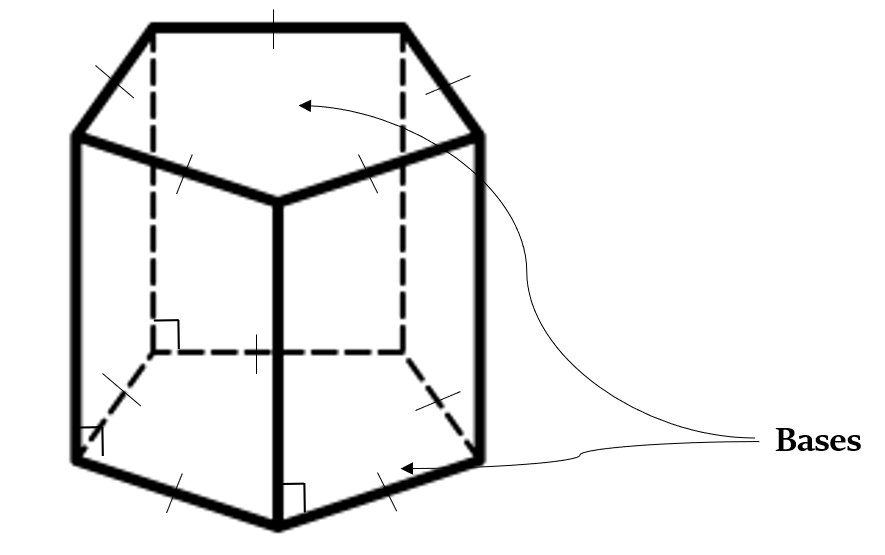
Regular Prism: It is a prism whose bases are regular figures, i.e. all sides of its both bases are equal.
Formulae related to Prisms
Formula 1: Volume
Volume of a Prism = Base Area × Height
Formula 2: Surface Area
Lateral surface area (i.e. area of the side faces) = Perimeter of base × Height
Total surface area = Lateral surface area + 2 × Area of base
Types of Prisms as per their Bases
We already know that, bases of a prism are polygons of any number of sides.
So, based on the kind of bases, we get various types of prisms.
- Triangular prism - has triangular bases with 3 sides.
- Rectangular or Square prism - has square/rectangular bases with 4 sides.
- Pentagonal prism - has pentagonal bases with 5 sides.
- Hexagonal prism - has hexagonal bases with 6 sides.
- and so on …..
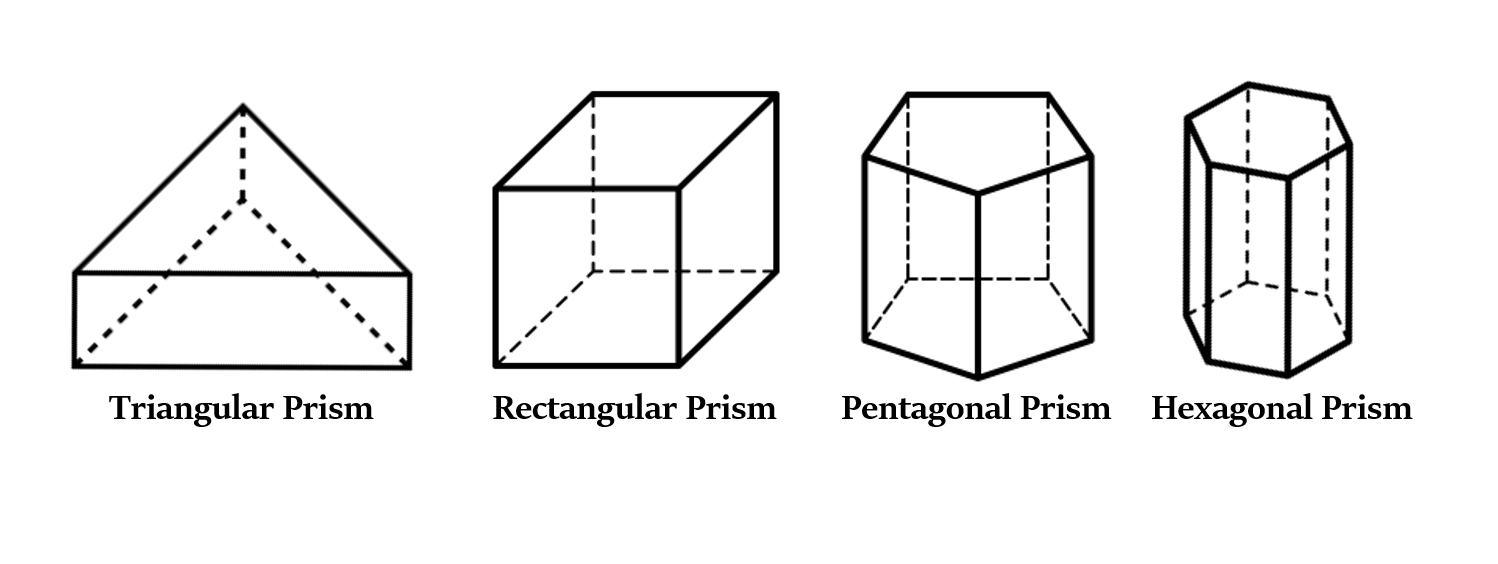
We will study some of these prisms in more detail in subsequent articles.